
- USB DRIVE FORMAT FAT32 OR NTFS UPDATE
- USB DRIVE FORMAT FAT32 OR NTFS SOFTWARE
- USB DRIVE FORMAT FAT32 OR NTFS WINDOWS
Read/write files larger than 4 GB and up to maximum partition sizeīetter space management = less fragmentationĪllows more clusters on larger drives = less wasted spaceĪdd user permissions to individual files and folders (Windows Professional) So what is the difference between those file systems and which one should you choose? Let's look at the benefits of each.

You will not see FAT and FAT32 if your drive is larger than 32 GB.
USB DRIVE FORMAT FAT32 OR NTFS WINDOWS
Notes: When formatting flash drives under Windows, most OSes will pickup allocation size of 4096, which is a good default for the majority of situations.In Windows 10, you will see a maximum of four different file systems: NTFS, FAT, FAT32, and exFAT. For large flash drives where files over 4GB are necessary, you should read the notes above carefully to weigh the pros and cons of exFAT vs. In conclusion, the most compatible and flash-media friendly format is FAT32. Still, it is a good choice if you are not concerned about the read-only Max OS-X limitation. NTFS is not as flash media friendly as FAT32/exFAT because of journaling/extra disk writes. NTFS partitions mount as read-only in OS X (unless you modify the fstab). NTFS - journaling file system with more disk writes, you should use "safely disconnect drive" instead of simply unplugging USB flash drives to make sure you do not corrupt any data.
USB DRIVE FORMAT FAT32 OR NTFS SOFTWARE
Note: Some backup software may have issues recognizing/reading/booting from exFAT flash drives when outside of Windows, so thorough testing should be performed to ensure compatibility. It has been adopted by the SD Card Association as the default file systems for SDXC cards larger than 32GB. OS X Snow Leopard in 10.6.5 and later supports exFAT. Most Linux/FreeBSD distributions can read/write using fuse-exfat (not as an official part of Linux because of the MS patents).
USB DRIVE FORMAT FAT32 OR NTFS UPDATE
exFAT can be read on most newer OSes (Windows XP/2003 needs update KB955704, Windows Vista needs SP1). The only downside less compatibility than FAT32.

Theoretically it has smaller footprint than NTFS, no journaling (can unplug device without losing data), and it can be read on OS X 10.6.5 (NTFS is read-only unless you modify the fstab).

exFAT - Microsoft proprietary extension to FAT32 designed for flash drives, allows for files larger than 4GB, and much larger partition size than FAT32. There are third party tools that can create larger Fat32 partitions, most operating systems support partitions up to 2TB. It is a choice by Microsoft to promote NTFS, which is generally more efficient when working with large partitions. In addition, Windows can't create FAT32 partitions over 32GB, but it can still read/write to them (Windows 98 could create up to 128GB FAT32 partitions). Its only notable limitation is that any single file can't be larger than 4GB. FAT32 - It is currently the default file system for USB drives and flash cards smaller than 32GB. The root folder can manage a maximum of 512 entries.
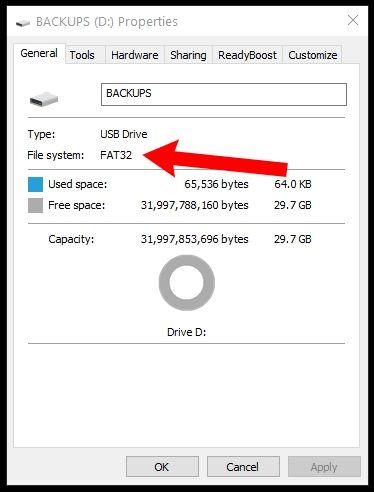
It uses larger default cluster sizes (up to 32kb) compared to FAT32 (4kb) to increase speed but reduce efficiency. FAT16 - an older format limited to 4GB size. With this, choosing the right file system when formatting your drive becomes very relevant, and below are the pros/cons to using the most common types. Large USB flash drives are becoming very popular as storage and backup media.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
